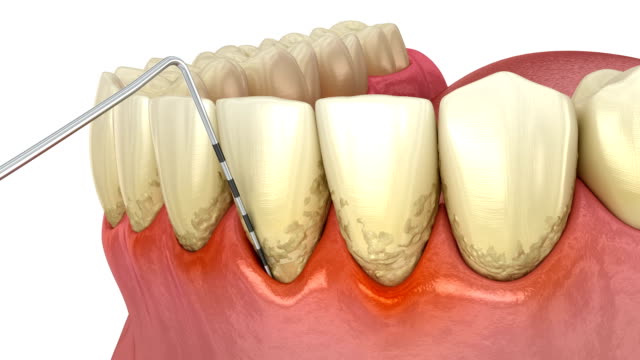
Gingivitis symptoms is a common oral health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by inflammation of the gums, primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque on the teeth. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress and lead to more severe oral health problems, including tooth loss. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the symptoms of gingivitis and the role of dental bone grafting in addressing this condition.
Gingivitis Symptoms
Gingivitis is often referred to as the earliest stage of gum disease. Recognizing its symptoms is crucial for timely intervention and prevention of further complications. Below are some common gingivitis Symptoms:
Bleeding Gums One of the hallmark signs of gingivitis is bleeding gums, particularly when you brush or floss your teeth. Healthy gums should not bleed during routine oral care. If you notice blood on your toothbrush or in the sink after brushing, it may be an indicator of gingivitis.
Swollen and Red Gums Healthy gums should have a pinkish hue and a firm texture. In the case of gingivitis, the gums may appear swollen and red due to inflammation. This swelling can make your gums look puffy and more pronounced.
Bad Breath (Halitosis) Persistent bad breath, or halitosis, can be a symptom of gingivitis. The bacteria in the plaque and tartar buildup release foul-smelling gases, causing unpleasant breath. If you’ve noticed chronic bad breath despite maintaining good oral hygiene, it may be time to consult a dentist.
Tender Gums Gingivitis can make your gums sensitive and tender to the touch. This tenderness may make it uncomfortable when eating or during oral care routines.
Gum Recession As gingivitis progresses, the gum line may start to recede, exposing more of the tooth’s root. This can lead to increased tooth sensitivity and further complications if not addressed.
Pus Formation In severe cases of gingivitis, pockets of pus may form between the teeth and gums. This condition is known as “abscessed gums” and requires immediate dental attention.
The Importance Of Dental Bone Grafting
While gingivitis can often be treated with improved oral hygiene practices and professional cleanings, advanced cases may lead to the loss of supporting bone structure. In such instances, dental bone grafting becomes essential. Let’s delve into the significance of dental bone grafting in the context of gingivitis.
Restoring Lost Bone Tissue Advanced gingivitis can result in the deterioration of the bone that holds your teeth in place. Dental bone grafting involves the transplantation of bone tissue to rebuild the lost bone, providing necessary support for the teeth.
Enhancing Dental Implant Success In cases where tooth loss has occurred due to severe gingivitis, dental implants are often the preferred choice for tooth replacement. Dental bone grafting can create a stable foundation for the implant, increasing the chances of successful implantation.
Preventing Tooth Mobility Gingivitis can weaken the attachment of teeth to the surrounding bone, leading to tooth mobility. Dental bone grafting can help stabilize teeth, reducing the risk of tooth loss.
Improving Aesthetics Bone loss resulting from gingivitis can affect the appearance of your smile. Dental bone grafting can restore the natural contours of your jawbone, enhancing your overall facial aesthetics.
The Dental Bone Grafting Procedure
Now that we understand the importance of dental bone grafting let’s take a closer look at the procedure itself:
Consultation and Evaluation Before undergoing dental bone grafting, a thorough consultation with a periodontist or oral surgeon is necessary. They will assess the extent of bone loss and determine the most suitable grafting technique.
Graft Material Selection There are various sources of graft material, including your own bone (autograft), donor bone (allograft), or synthetic materials (alloplast). The choice of graft material depends on your specific case and preferences.
Anesthesia Local or general anesthesia is administered to ensure the procedure is pain-free. Your dental specialist will discuss the anesthesia options with you beforehand.
Graft Placement The graft material is placed in the area of bone loss, either directly on the existing bone or within a prepared site. Your specialist will secure the graft in place using sutures or special membranes.
Healing and Integration Over the following months, the graft material will gradually integrate with your natural bone. This process promotes the regeneration of new bone tissue.
Follow-up Appointments Regular follow-up appointments with your dental specialist are essential to monitor the progress of healing and ensure the success of the grafting procedure.
Recovery And Aftercare
After undergoing dental bone grafting, it’s crucial to follow proper aftercare instructions to promote optimal healing and long-term success:
Pain Management You may experience some discomfort and swelling after the procedure. Your dentist will prescribe pain medication and provide guidelines for managing pain.
Diet Modifications Soft foods are recommended during the initial stages of recovery to avoid putting excessive pressure on the graft site. Gradually reintroduce a normal diet as advised by your dental specialist.
Oral Hygiene Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is essential during the healing process. However, be gentle when brushing and flossing around the graft site to prevent disruption.
Avoiding Tobacco and Alcohol Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can hinder the healing process. It’s advisable to abstain from these habits during your recovery.
Follow-up Visits Regularly scheduled follow-up visits allow your dental specialist to monitor your progress and address any concerns promptly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of gingivitis and seeking timely treatment is crucial to prevent its progression. For advanced cases that result in bone loss, dental bone grafting plays a pivotal role in restoring oral health and preventing tooth loss. By understanding the symptoms, the importance of dental bone grafting, and the procedure itself, individuals can take proactive steps to address gingivitis and maintain a healthy smile. If you suspect you may have gingivitis or require dental bone grafting, it is essential to consult with a qualified dental professional for a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.